Wednesday, July 3, 2019
L’arthrose est une maladie courante chez les chevaux de sport, due dans la plupart des cas à un surentraînement ou à une mauvaise alimentation. Seaver vous permet de surveiller l’état de santé de votre cheval afin de limiter l’apparition d’arthrose.
Dans une articulation, le cartilage sert d’amortisseur, il permet d’éviter les frottements entre les deux os et d’amortir les chocs lors du mouvement. L’arthrose est une maladie qui entraîne une dégénérescence de ce cartilage. L’espace articulaire va se réduire et le liquide synovial (liquide permettant de réduire la friction dans l’articulation) va s’épancher. L’articulation sera moins lubrifiée et va venir se bloquer. L’arthrose peut s’accompagner d’une ossification des articulations (bout d’os en trop dû à une calcification).
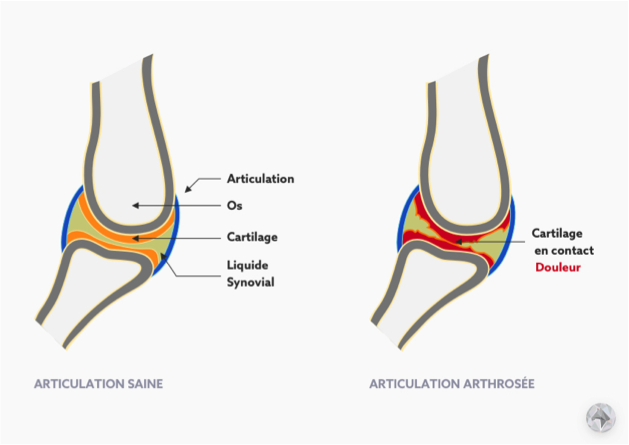
Les deux os ont du mal à s’articuler l’un par rapport à l’autre. Cela va créer une inflammation au niveau de l’articulation et va entraîner des douleurs.
C’est une maladie courante chez les chevaux âgés ou ayant une activité physique soutenue.
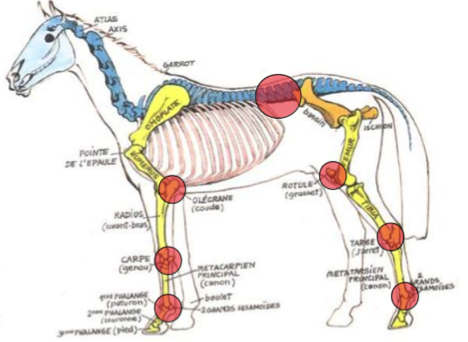
Les zones les plus sensibles sont les articulations des membres (jarret, rotule, boulet, genoux, …) et le dos (en particulier la jonction thoraco-lombaire).
C’est une maladie irréversible mais dont l’évolution peut être ralentie.
Les causes de l’arthrose sont diverses, on peut parfois mettre en cause le travail du cheval, son physique ou certains agents extérieurs.
Si le cavalier demande à son cheval un effort physique soutenu trop fréquemment, la musculature de celui-ci va travailler de manière excessive. L’articulation va compenser le travail non réalisé par les muscles. Hors ce n’est pas son rôle et c’est pour cette raison que cela peut provoquer de l’arthrose. Une boiterie ou une compensation musculaire du cheval due à une blessure par exemple peut, pour les mêmes raisons, provoquer de l’arthrose, il faut donc essayer d’en limiter l’apparition.
Ces médicaments vont masquer la douleur mais cela ne veut pas dire pour autant que la zone en question est totalement guérie. Il faut donc faire attention à reprendre le travail progressivement.
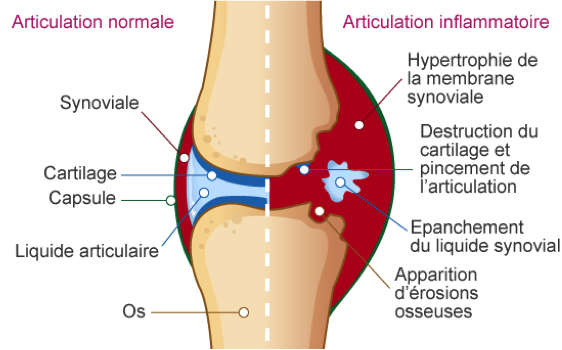
L’inflammation d’une articulation liée à une entorse, une luxation ou autre peut aussi provoquer de l’arthrose si celles-ci sont trop consécutives. Lorsqu’une articulation est enflammée, la membrane synoviale va s’épaissir et compresser l’articulation. Cela entraîne une destruction du cartilage et peut à long terme provoquer de l’arthrose.
Lorsque le cheval est en mouvement, il compense la dureté ou la souplesse du sol à l’aide de ses articulations. Travailler sur un sol trop dur ou trop mou va entraîner une sursollicitation des articulations qui peut engendrer de l’arthrose.
À l’inverse d’une surcharge de travail, un manque de mouvement du cheval peut provoquer de l’arthrose. En l’absence de stimulation, l’os perd peu à peu toute organisation et toute force. Un petit choc sera perçu comme gros pour l’articulation.
Certaines causes physionomiques d’arthrose sont génétiques. Dans le cas d’arthrose primaire, les chevaux ont leur cartilage moins robuste que la moyenne. Ces chevaux peuvent avoir de l’arthrose, malgré une activité physique modérée et un très bon entretien.
L’ostéochondrose est une maladie génétique qui se développe chez les poulains. Cette maladie est l’une des causes de l’arthrose. Elle entraîne chez le poulain une croissance importante de ses os ce qui provoque des suros. Ceux-ci peuvent s’effriter et venir se loger dans l’articulation ce qui entraîne une inflammation de l’articulation.
Un cheval avec de mauvais aplombs va avoir plus facilement de l’arthrose qu’un cheval avec de très bons aplombs, il va falloir faire plus attention pour en limiter le développement.
Le cartilage va s’user plus vite à l’endroit de l’articulation où la pression est la plus forte et il y aura donc apparition d’arthrose.
Un surpoids peut entraîner une fatigue musculaire très importante et donc de l’arthrose. Cette maladie peut aussi être due à un mauvais entretien du pied. Par exemple, un pied trop haut ou trop long modifie l’axe inter-phalangien. Un parage asymétrique (talon plus haut d’un côté), provoque une compression articulaire d’un côté et peut aussi entraîner de l’arthrose chez le cheval
Certains médicaments peuvent entraîner des inflammations aux articulations et provoquer de l’arthrose. Une infiltration faite à votre cheval peut soulager l’arthrose (ou la limiter) mais peut aussi l’aggraver. Une articulation est un endroit stérile, il faut donc faire très attention lors de l’implantation de la seringue. Celle-ci doit être parfaitement stérile. La moindre bactérie en contact avec l’articulation pourrait provoquer son inflammation.
Certaines hormones régulent les équilibres en minéraux du corps mais peuvent provoquer une croissance osseuse trop importante ou une destruction osseuse.
Le vétérinaire est généralement celui qui va diagnostiquer l’arthrose grâce à une radiographie qui s’accompagne généralement d’une échographie si nécessaire. Le rôle du vétérinaire va être de soulager la douleur.
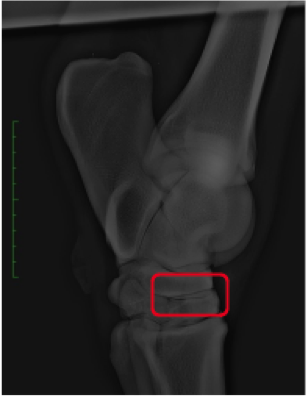
Pour cela, il existe plusieurs traitements possibles. Le cheval peut être mis sous anti-inflammatoires. Dans la plupart des cas le diagnostic d’arthrose s’accompagne d’une infiltration de corticoïdes. L’infiltration permet une réduction de la douleur immédiate ce qui est plutôt positif. Cependant, lors de l’infiltration, la piqûre dans l’articulation va l’abîmer. Celle-ci demande une grande attention. Il ne faut pas qu’il y ait de bactérie qui pénètre dans l’articulation. Cette technique dégrade l’articulation, il faut faire attention à ne pas infiltrer trop de fois le même endroit. Le vétérinaire peut aussi prescrire des compléments alimentaires afin de diminuer la douleur au niveau de l’articulation.
L’ostéopathe va soulager les compensations (musculaires, myofasciales, boiteries…) dues à l’arthrose. Cependant, l’ostéopathe ne va pas agir sur l’articulation mais sur les muscles adjacents. Ce sont des soins de conservation et/ou de prévention pour l’animal.
Le maréchal va venir modifier les aplombs du cheval grâce aux parages et aux fers. Avant que le cheval n’ait de l’arthrose, il va s’assurer de la symétrie du pied du cheval. Une fois que le cheval a de l’arthrose, le rôle du maréchal va être de soulager l’arthrose en modifiant la ferrure.
Il est possible de suivre le nombre de calories brûlées par votre cheval en temps réel grâce à la sangle Seaver. Cette fonctionnalité vous permet d’adapter l’alimentation de votre cheval en fonction de son activité et d’éviter un possible surpoids (cause possible de l’arthrose). Pour plus de détails, vous pouvez aller lire l’article : « Comment bien nourrir son cheval ? Nos conseils pour gérer votre cheval au box » dans le blog de notre site.
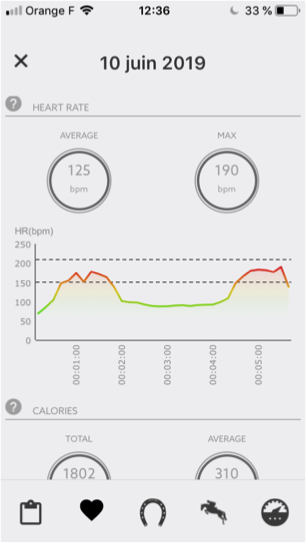
Il est aussi possible de suivre grâce à la sangle Seaver, le rythme cardiaque de son cheval. Un graphique représentant le rythme cardiaque au cours du temps et le rythme cardiaque moyen vous est affiché sur la page « cardio » de votre entraînement. Cette fonctionnalité vous permet de vérifier le rythme cardiaque de votre cheval au cours de l’entraînement et vérifier que vous ne surentraînez pas votre cheval trop souvent. En surveillant l’intensité du travail de votre cheval, vous pourrez éviter de lui imposer une charge de travail trop importante (cause possible de l’arthrose que nous souhaitons limiter). Pour plus d’informations, vous pouvez consulter notre article
sur notre blog.
Lors d’une séance à l’obstacle, vous pouvez aussi surveiller le nombre de sauts et aussi l’énergie absorbée à la réception. Les efforts de sauts répétés sont une cause possible d’arthrose. Sur une séance classique, on conseillera de ne pas dépasser environ 50 sauts et un total des chocs à la réception de 70kJ. Pour en savoir plus, vous pouvez aller lire l’article « Utiliser les indicateurs de saut Seaver dans son travail à l’obstacle » sur notre blog.

Seaver vous permet d’avoir une vision précise de la locomotion de votre monture grâce à la détection de la symétrie au trot en ligne droite et du décalage en saut.
Cette fonctionnalité ne pourra cependant pas vous dire exactement qu’il s’agit d’arthrose et il faudra de toute manière faire appel à un vétérinaire afin d’en être sûr. La sangle Seaver peut néanmoins vous alerter.
Un cheval avec de l’arthrose va avoir tendance à être
dissymétrique au trot et sur la poussée d’un saut.

Comme on peut le voir sur ce cheval atteint d’arthrose au jarret gauche, il y a plus de sauts pour lesquels il y a un décalage à gauche. On voit aussi une dissymétrie entre le diagonal droit et le diagonal gauche. Plus que la valeur de la symétrie, c’est sa diminution systématique qui doit vous alerter. De même pour le décalage en saut, il est normal d’observer parfois un décalage. Mais c’est quand cela devient récurrent qu’il faut se poser la question.
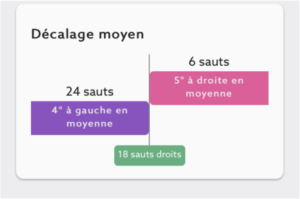
⚠ Ce n’est pas parce que vous avez ces résultats que votre cheval a forcément de l’arthrose. Beaucoup d’autres facteurs peuvent être à l’origine du décalage du cheval. Il faut forcément demander l’avis d’un vétérinaire.
See you soon for a new article,
L’équipe Seaver 😉